Introduction
What Is Biometric Data Collection: Biometric data collection refers to the process of gathering and storing unique physical or behavioral characteristics of individuals for identification and authentication purposes. These characteristics can include fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, voiceprints, and even DNA. Biometric data collection has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its ability to provide a high level of security and accuracy in various applications.
One of the key advantages of biometric testing collection is its ability to provide a unique and unchangeable identifier for each individual. This makes biometric data collection a highly secure method of identification and authentication.
What is an example of biometric data?
Security systems and authentication processes leverage these traits to restrict access to resources and information. Biometric data includes fingerprints.
Fingerprints are unique and can identify a person. Ink and paper, optical scanners, and capacitive sensors can collect fingerprints.
Another biometric example is facial recognition. This technology analyzes and compares facial traits like eye distance, nose shape, and face contours using algorithms. Mobile devices, surveillance systems, and access control systems use facial recognition for authentication.
Biometric data can also include iris recognition, which uses eye color patterns to identify people. Border control and national identification programs use iris recognition, one of the most accurate biometric technologies.
Voice recognition and gait recognition are other biometric data types. These biometric methods are less widespread but can add security in some applications.
What are 3 examples of biometric data?
Here are three examples of biometric data:
1. Fingerprint:
Fingerprint recognition systems compare the captured fingerprint with the stored templates to verify or identify individuals.
2. Iris:
Recognition is another example of biometric data. Iris recognition systems capture high-resolution images of the iris and analyze its patterns to create a template.
3. Voice:
Voice biometrics involves analyzing the unique characteristics of an individual’s voice, such as pitch, tone, and pronunciation.
How is biometric data collected and stored?
These gadgets record fingerprints, iris patterns, and faces.
Example: speech and gait analysis. Voice recognition uses pitch, tone, and pronunciation to build a voiceprint. Gait analysis can identify a person by how they walk.
A safe database or system stores biometric data after collection. Protecting data from unauthorized access and tampering.
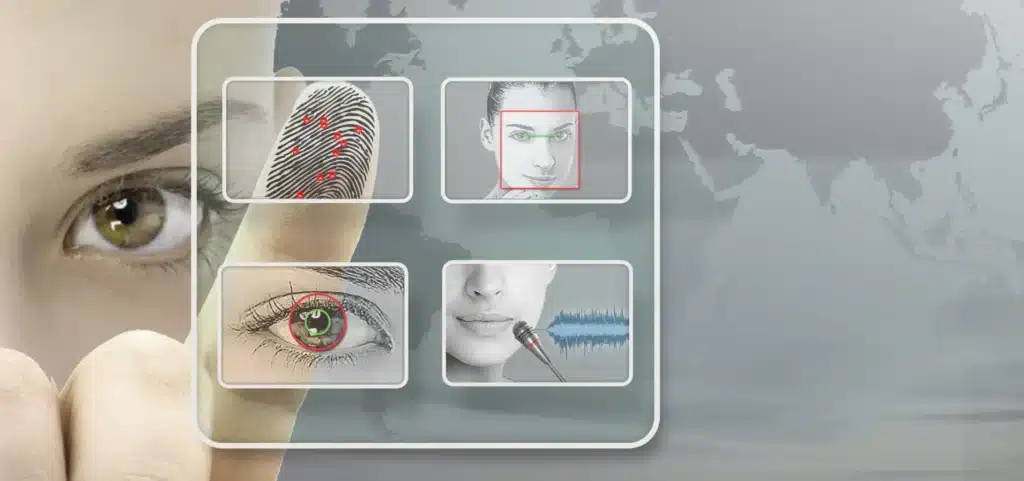
What are the 4 main types of biometrics?
Biometrics measures and analyzes individual physical or behavioral traits. The four main biometrics are fingerprint, face, iris, and voice recognition.
One of the oldest and most popular biometric technologies is fingerprint recognition. It entails photographing and analyzing fingertips’ unique patterns and ridges. Access control systems and mobile devices use fingerprint recognition because it is accurate and reliable.
Another popular biometric technique is facial recognition, which uses an individual’s unique facial features to identify and authenticate them. It involves photographing or videoing a person’s face and matching it to a database of known faces.
Iris identification uses an individual’s unique iris patterns and traits to identify and authenticate them. The colorful iris of the eye has complicated patterns that are unique to each person. Border control and national identification systems use iris recognition because it is accurate and secure.
What are the 2 categories of biometric data?
There are two main categories of biometric data: physiological and behavioral.
Physiological biometric data includes characteristics that are related to the physical attributes of a person’s body. This can include fingerprints, facial features, hand geometry, iris patterns, and DNA.
Behavioral biometric data refers to characteristics that are related to an individual’s behavior or actions. This can include their voice, signature, typing rhythm, gait, and even their keystroke dynamics.
Both physiological and behavioral biometric data have their own advantages and limitations. However, they may require specialized hardware or equipment for collection and can be more invasive.
Biometric data collection serves the purpose of identifying and verifying individuals based on their unique physical or behavioral characteristics. By using biometric data, organizations can ensure accurate identification and authentication, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
Moreover, biometric data collection also aims to improve convenience and efficiency in everyday activities. This eliminates the need for traditional passwords or PINs, making the process faster and more user-friendly.
How is biometric data collected?
Sensors or scanners can capture an individual’s distinctive physical or behavioral traits. Iris scanners record a person’s unique iris patterns, while fingerprint scanners capture fingertip ridges and patterns.
Cameras or video surveillance can also capture biometric data. Facial recognition technology can construct a biometric template using a person’s unique traits, such as eye distance and nose shape.
Voice recognition technology can assess a person’s pitch and tone to obtain biometric data. Use microphones or voice recorders.
What are some common applications of biometric data collection?
Industry and industry applications for biometric data collecting are numerous. Common uses include law enforcement and security. Fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans can correctly identify people and connect them to criminal records or watchlists.
This data can help doctors diagnose, customize, and improve patient care. However, organizations must prioritize privacy and data protection to ensure the responsible and ethical use of biometric data.
Financial institutions employ biometric data for identification verification and fraud prevention. The technology adds security and prevents identity theft and fraud.
What are the potential benefits and risks associated with biometric data collection?
Biometric data collection offers several potential benefits in various fields. Biometric identifiers, such as fingerprints or iris scans, are unique to each individual, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive information or restricted areas. This can be particularly useful in high-security environments, such as government facilities or financial institutions, where traditional forms of identification may be more susceptible to fraud or theft.
Another benefit of biometric data collection is convenience. Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, can provide a quick and seamless way for individuals to access their devices, accounts, or physical spaces. This eliminates the need for remembering complex passwords or carrying physical identification cards, improving user experience and efficiency.
However, along with these benefits, there are also risks associated with biometric data collection. One major concern is the potential for misuse or unauthorized access to biometric information. Additionally, there is a risk of false positives or false negatives in biometric systems, which can lead to denial of access for legitimate individuals or unauthorized access for impostors.
How is biometric data stored and protected to ensure privacy and security?
Biometric data, such as fingerprints, iris scans, and facial recognition patterns, is highly sensitive and requires robust storage and protection measures to ensure privacy and security. Organizations that collect biometric data must adhere to strict protocols to safeguard this information from unauthorized access and potential misuse.
Biometric data is often encrypted. This includes encoding the data in a key-protected format. Data intercepted by unauthorized parties is unreadable and useless with encryption.
Biometric data protection also requires effective access controls. Multi-factor authentication requires many kinds of identification to access data.These authentication layers greatly limit the risk of unwanted access.

Conclusion
Biometric data collection refers to the process of gathering and storing unique physical or behavioral characteristics of individuals for identification and authentication purposes. This data can include fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, voiceprints, and even DNA. The collection of biometric data has become increasingly prevalent in various industries, including law enforcement, healthcare, and financial services.
One of the main advantages of biometric data collection is its accuracy and reliability. This makes it a highly secure method of authentication, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. Additionally, biometric data collection can provide real-time identification, allowing for quick and efficient access to secure areas or systems.
However, the collection of biometric data also raises concerns regarding privacy and data protection. As biometric data is highly personal and sensitive, there is a risk of misuse or unauthorized access. It is crucial for organizations collecting biometric data to implement robust security measures and comply with relevant privacy laws and regulations. Additionally, individuals should be informed about the purpose and scope of biometric data collection and have the right to control and delete their data.
Biometric data collection is a powerful tool for identification and authentication purposes. Its accuracy and reliability make it a highly secure method of verifying individuals’ identities. However, organizations must prioritize privacy and data protection to ensure the responsible and ethical use of biometric data.

